Straw Insulation Fire Hazard

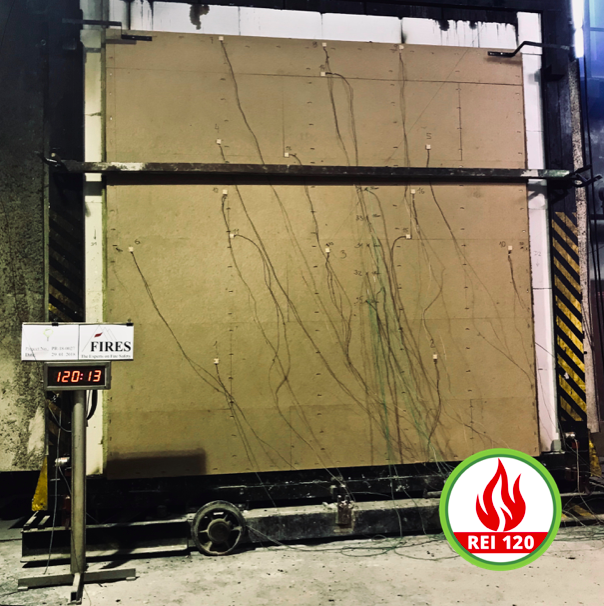
Three densities of compressed straw 75 125 and 175 kg m3 were selected and their combustion and thermal responses were evaluated at various scales in attempt to define the optimal density considering various factors.
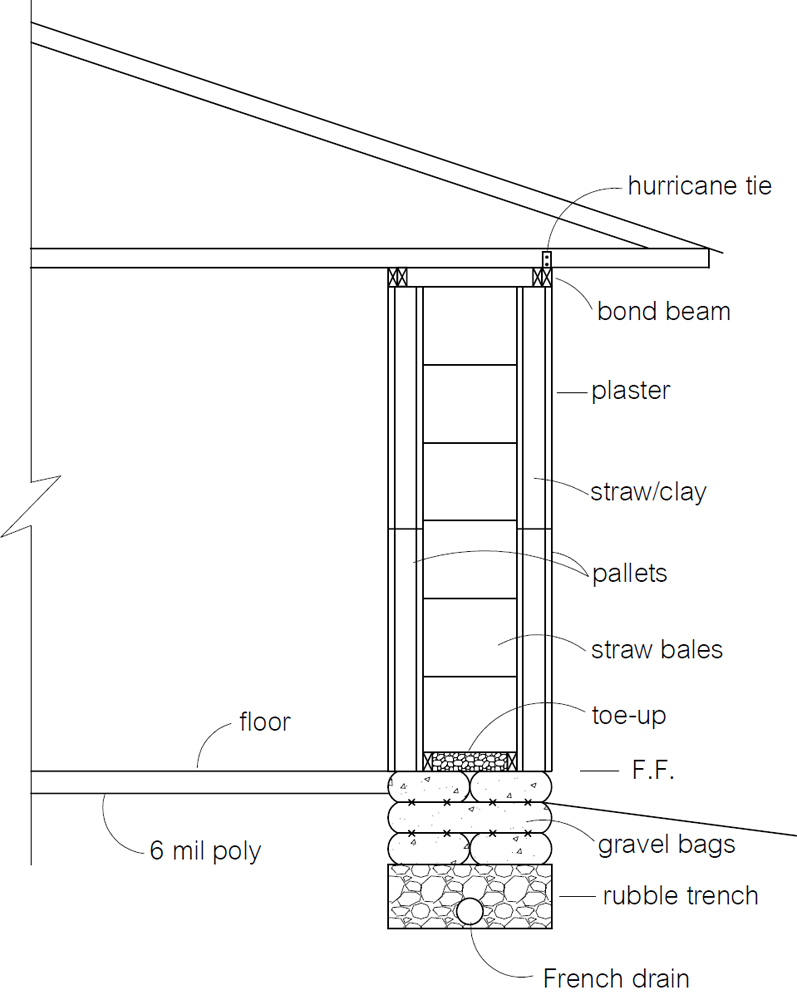
Straw insulation fire hazard. The objective of the study presented in this art icle is todocument fire hazards of compressed straw when used a s thermal and acousticinsulation within wood framed building assemblies. The most common chemicals used today in cellulose insulation are boric acid sodium borate borax and ammonium sulfate. One way to counter this is to stucco the soffits of the overhang. From an article in environmental building news ebn.
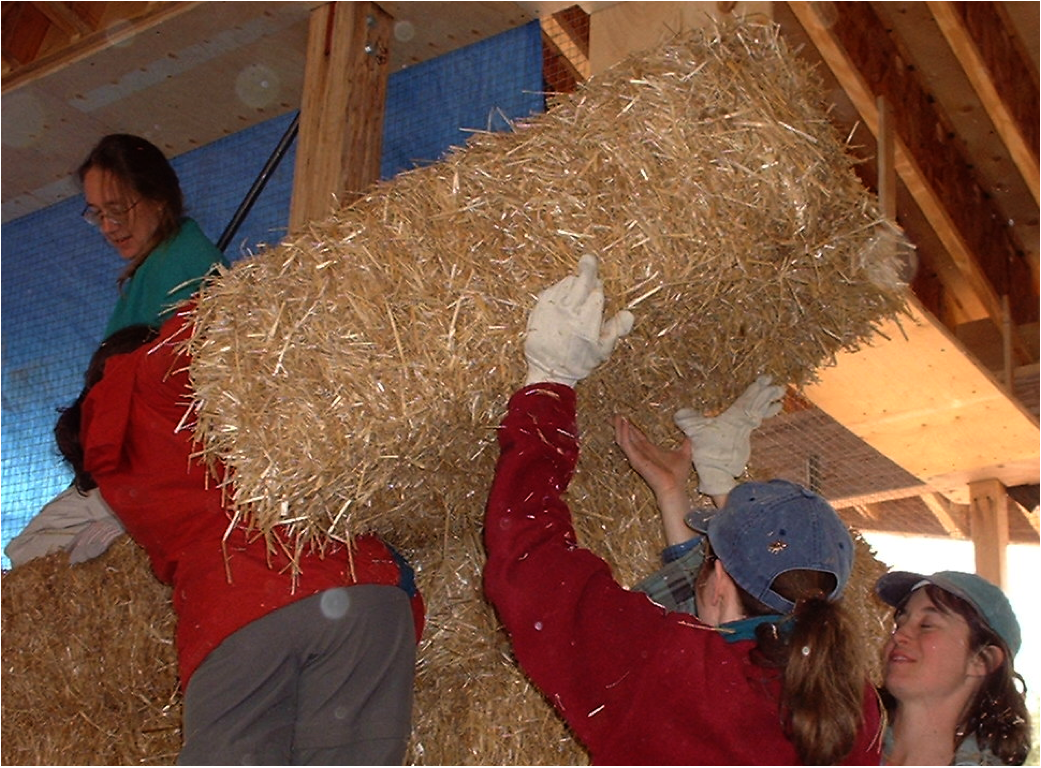
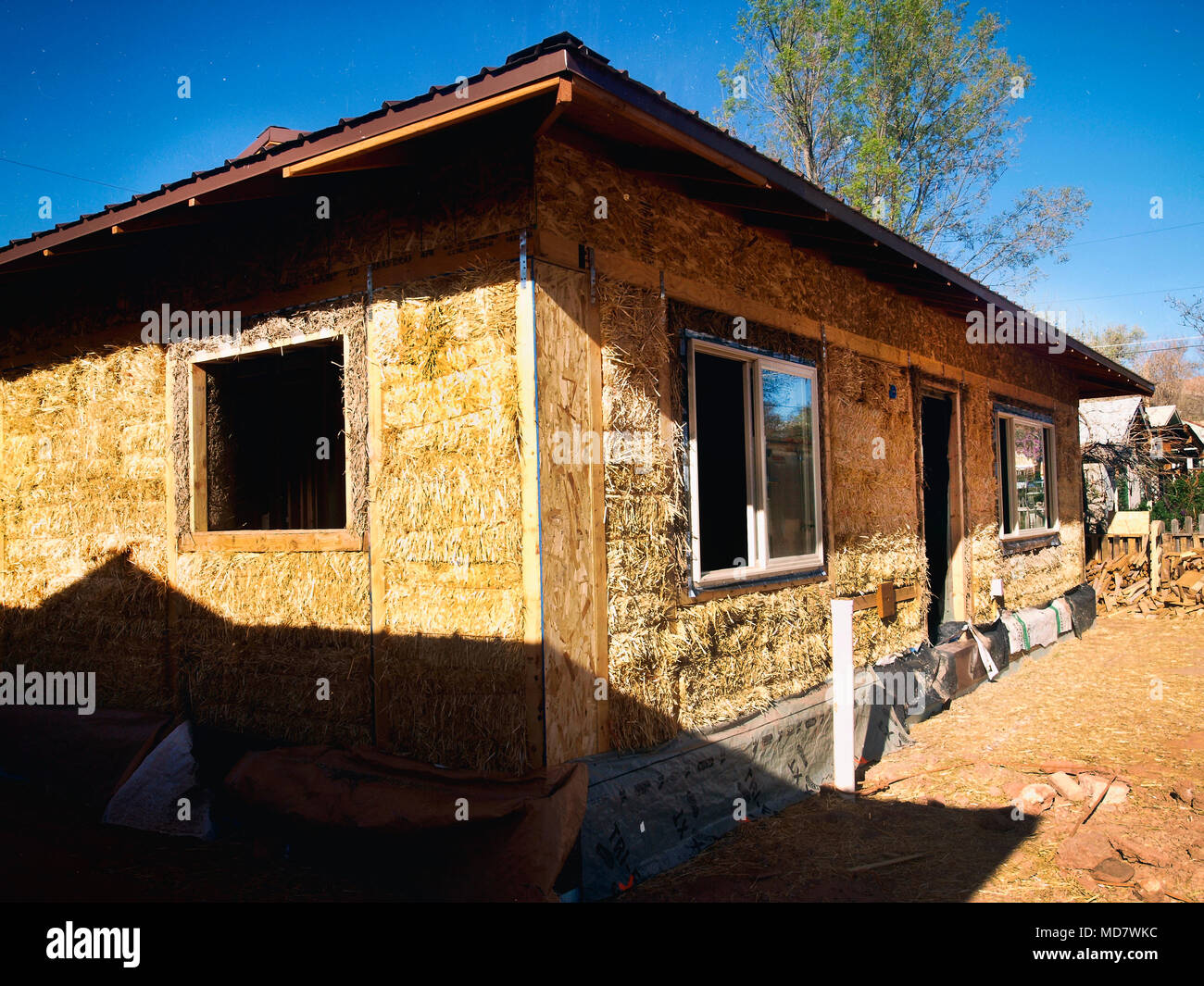
Loose straw is indeed flammable but the bales are so tightly packed that they actually increase fire resistance. The weakest part of straw bale homes in terms of fire is indeed the areas of wood the large overhangs being perhaps the most at risk. Boric acid and sodium borate have the advantage of not only providing fire retardancy. It might seem like straw bale houses pose a tremendous fire hazard but they provide roughly three times the fire resistance of conventional homes source.
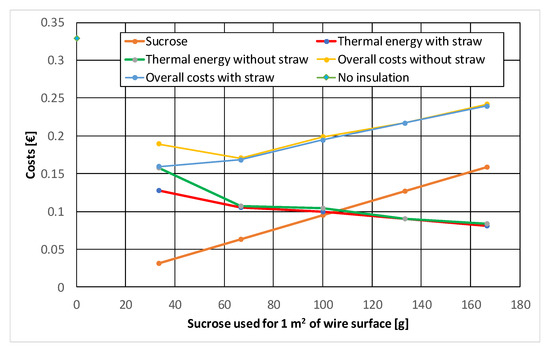
The construction sector continues to adapt to the challenges posed by climate change. Architects and engineers aim to build sustainable energy resource and cost efficient structures by increasingl. The results suggest that compressed may have similar or better behavior under the heating conditions investigated when compared to a commercially available combustible insulation material. I understand that straw bales would be too heavy and loose straw would be a fire hazard.
Cellulose insulation is typically around 20 fire retardant chemicals by weight. How ever fire safety has always been a significant concern for timber building con struction internationally. Couldn t i make blocks of it say 2 x3 x12 dry them thoroughly then install them in the attic. Wouldn t clay straw be light enough and fire resistant enough.
The objective of the study presented in this article is to document fire hazards of compressed straw when used as thermal and acoustic insulation within wood framed building assemblies. The compressed straw with a density of 75 kg m3was found to have the best behavior with respect to both reactions to fire and insulation properties. Insulation backing materials should be fire retardant and have a maximum flame spread rating of 25 when tested in accordance with astm e 84 standard test method for surface burning characteristics of building materials published by the american society for testing materials astm and as required by ul 723 standard for safety test for.