Irregular Gallbladder Wall Thickening Radiology
Gallbladder wall thickening can be caused by inflammatory benign and malignant etiologies.
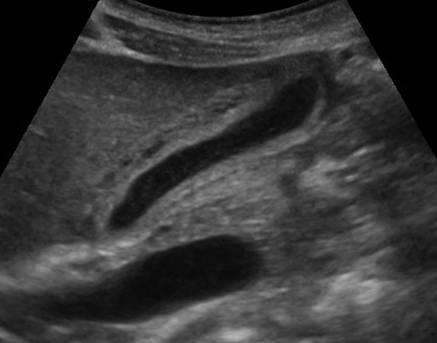
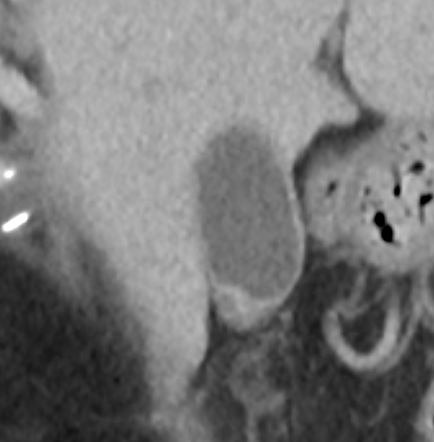
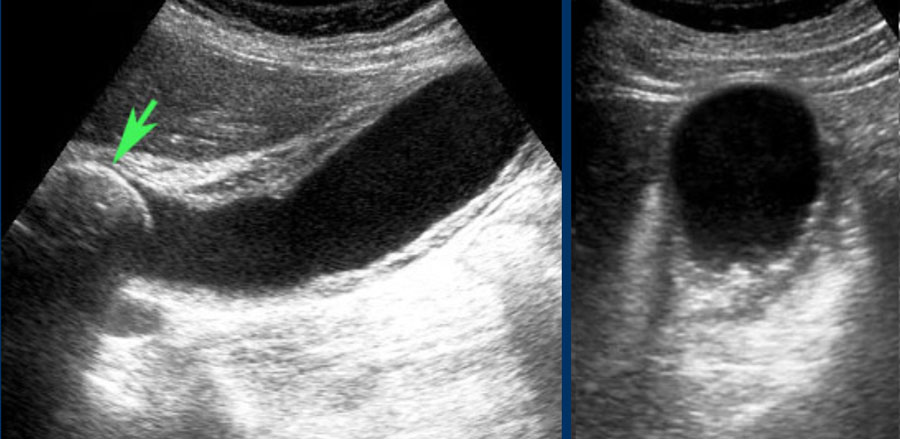
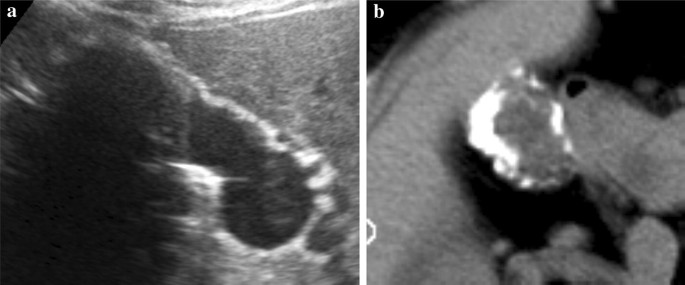
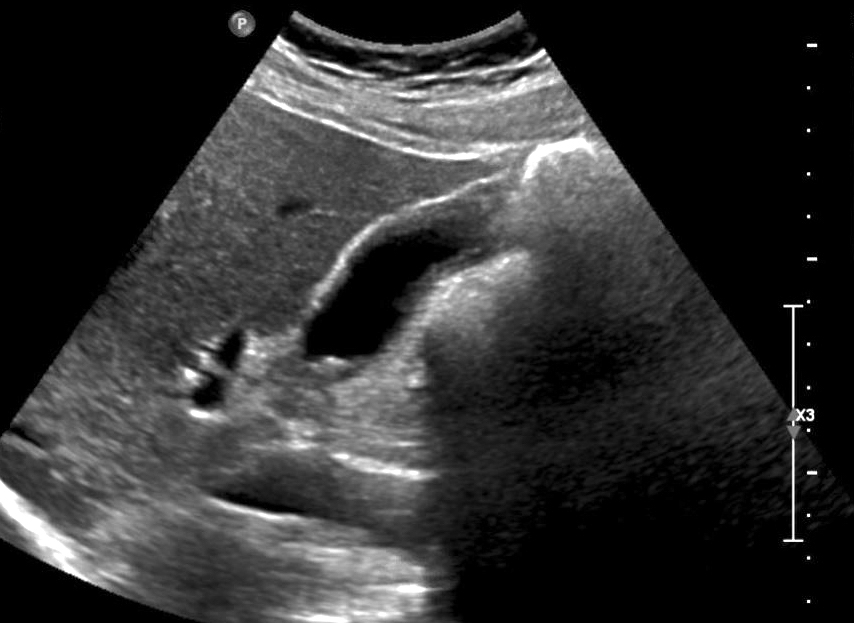
Irregular gallbladder wall thickening radiology. Noncancerous benign tumors include papillomas. Pseudothickening caused by the normal postprandial state of the contracted gallbladder is also extremely common 5. Thickening of the gallbladder wall is always abnormal although the significance of the thickening is highly dependent upon the underlying disease process. It is normally only about 1mm thick in the neonate.
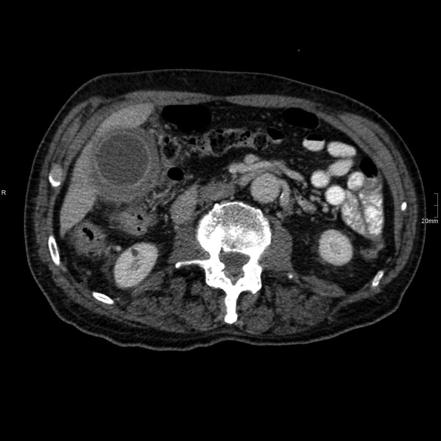
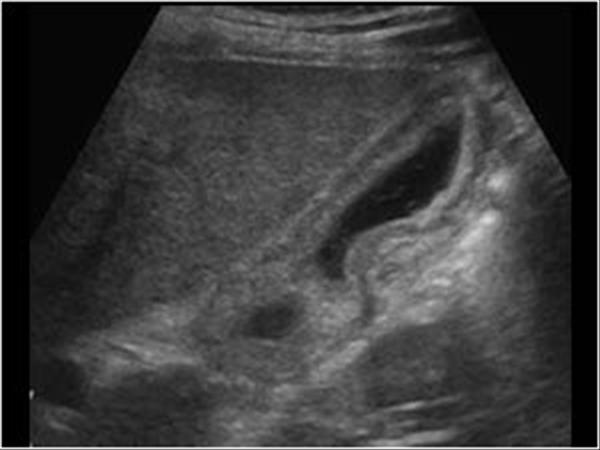
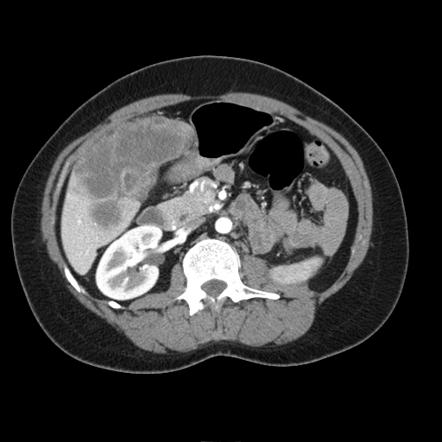
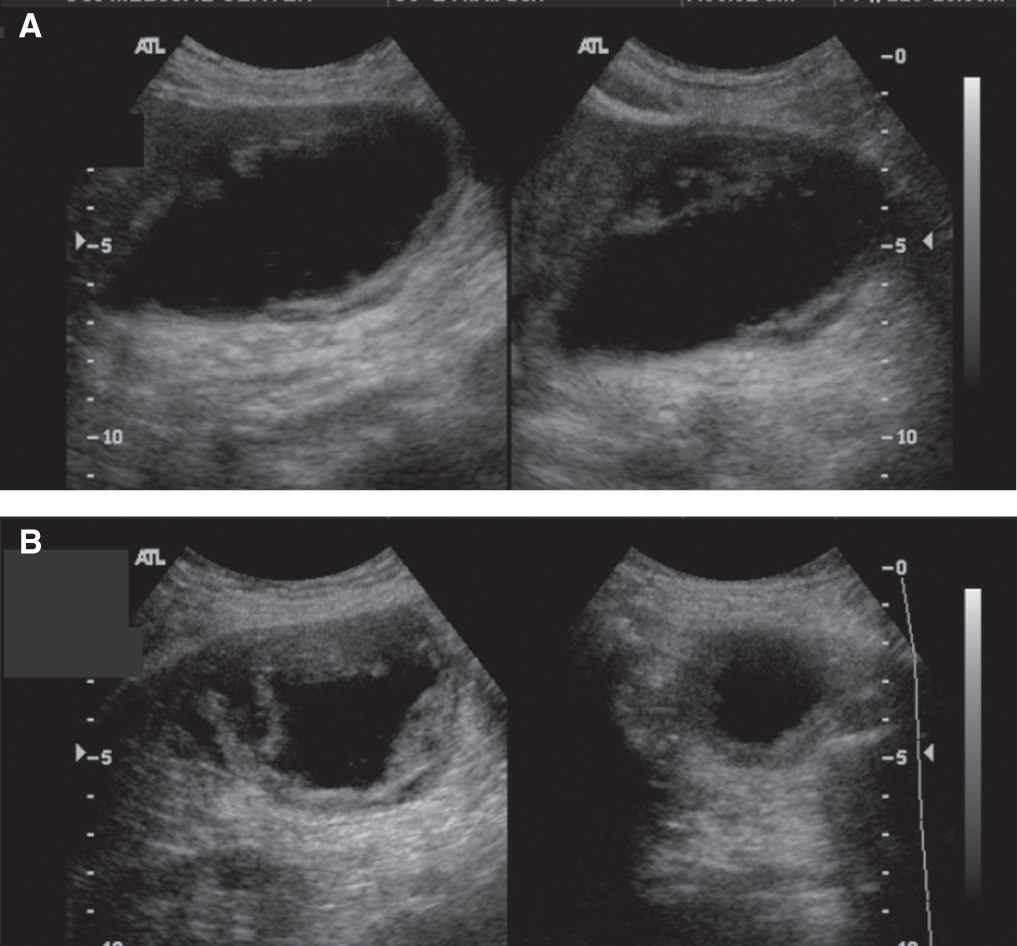
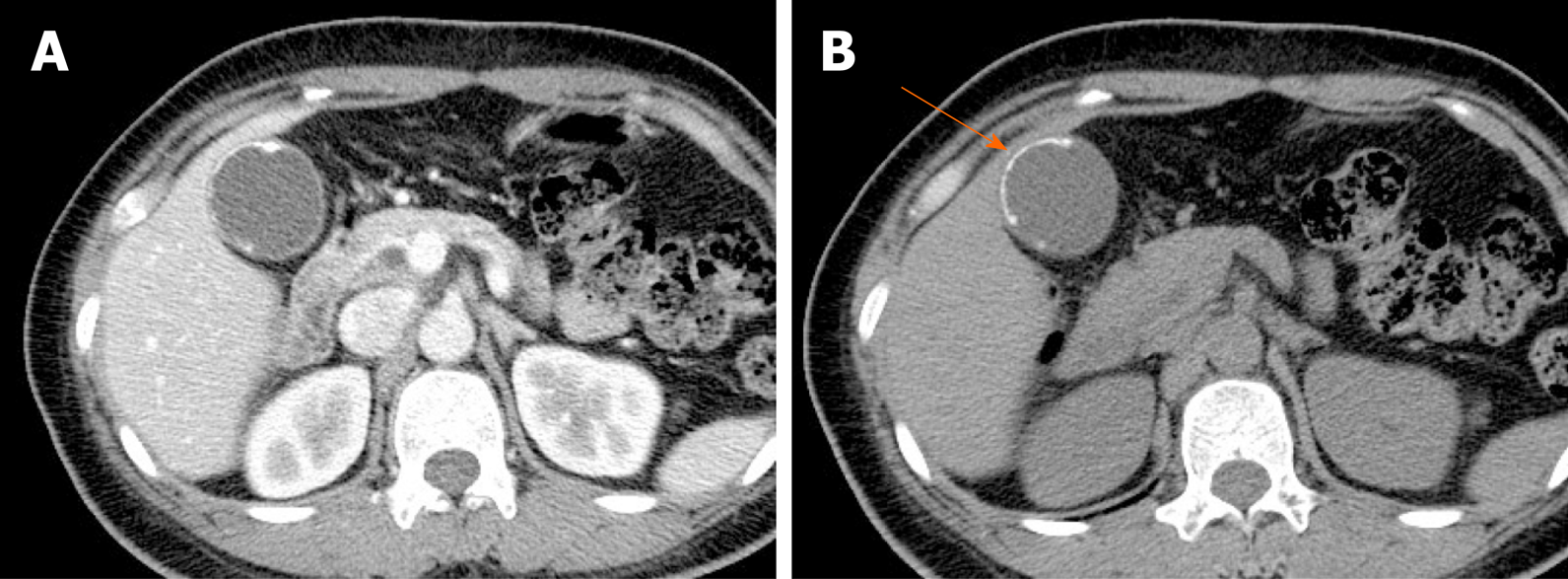
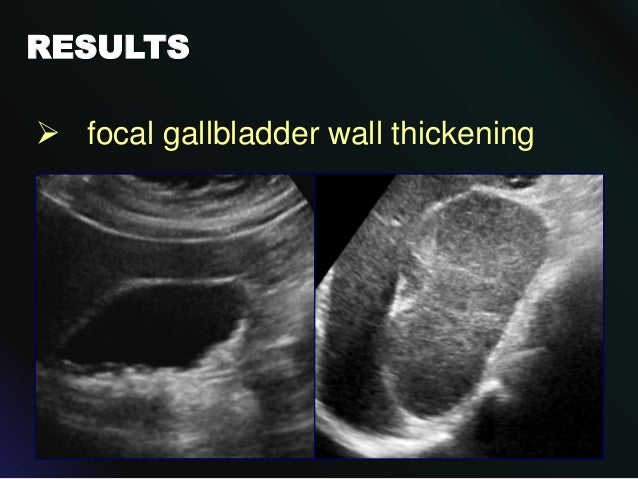
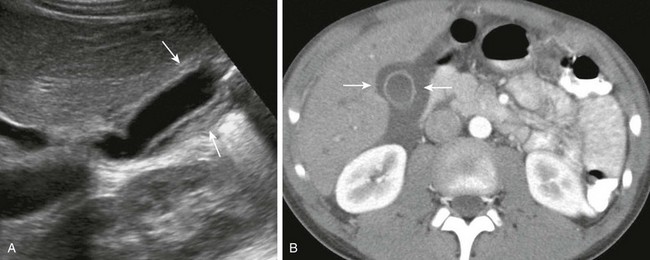
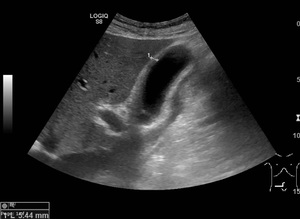
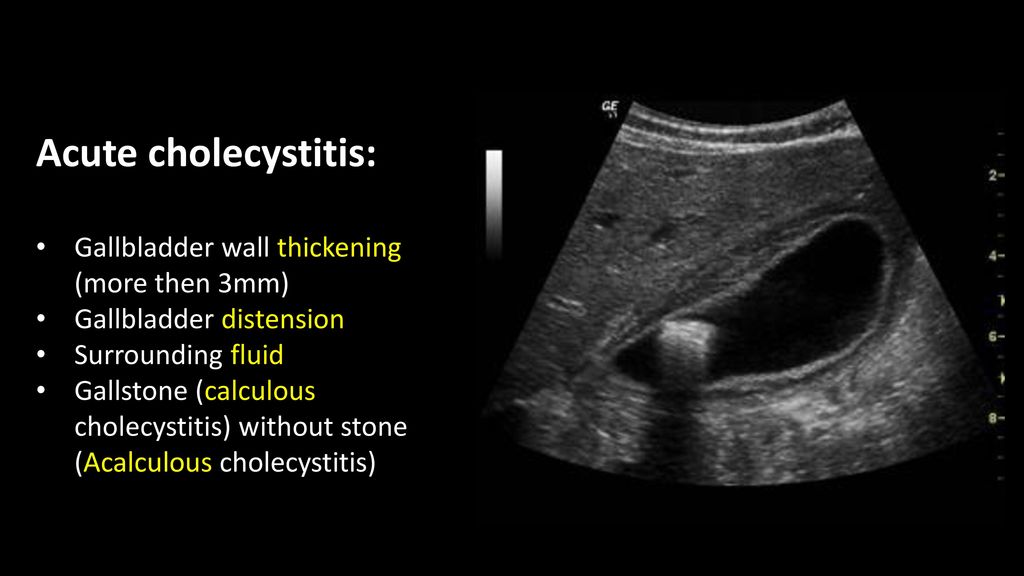
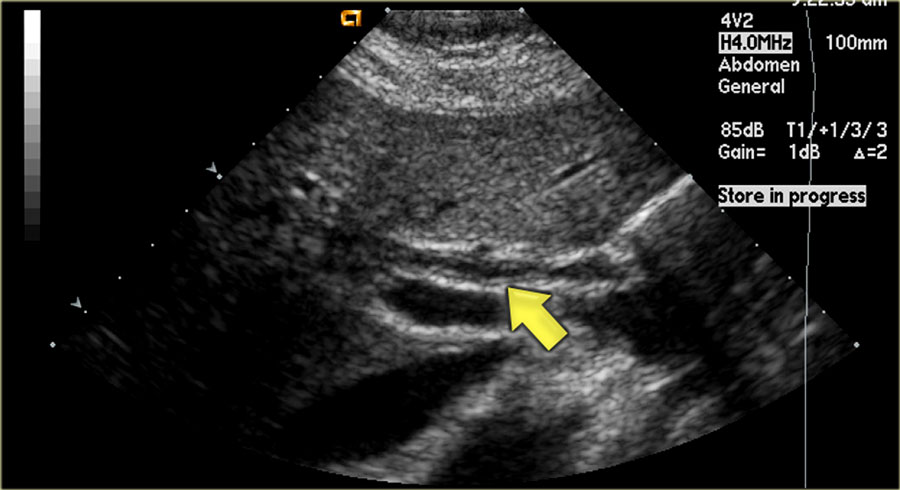
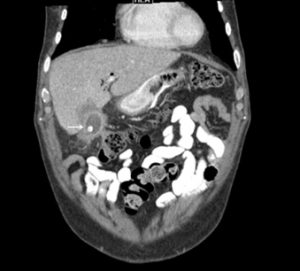
Several different possible imaging appearances mass completely replacing gallbladder gb 2 3 of cases irregular focal or diffuse gb wall thickening 20 30 intraluminal polyploid gb mass 20 of cases typically hypodense on venous phase but may have peripheral vascularity on arterial phase frequently invades liver and porta hepatis bulky porta hepatis paraaortic. It also may reflect secondary involvement of the gallbladder due to direct inflammatory spread from adjacent structures as in patients with pancreatitis acute hepatitis or severe pyelonephritis. Cholecystitis acute cholecystitis chronic cholecystitis gallbladder empyema 7 xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis 11 acalculous cholecystitis11 postprandial phy. A thickened gallbladder wall measures more than 3 mm typically has a layered appearance at sonography 1 and at ct frequently contains a hypodense layer of subserosal oedema that mimics pericholecystic fluid 2.
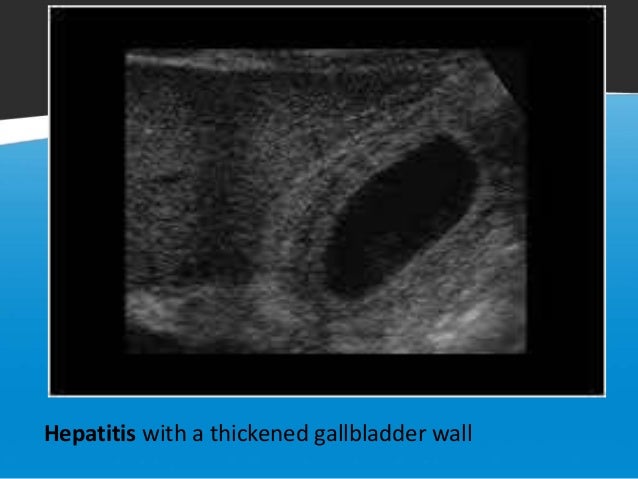
Diffuse gallbladder wall thickening 3 mm by ultrasound can be seen in such primary gallbladder inflammatory processes as acute chronic and acalculous cholecystitis. Thickening of the gallbladder wall usually considered 3 mm is a non specific sign of various conditions. Thickening of the gallbladder wall is a relatively frequent finding at diagnostic imaging studies. Abnormal tissue growth in the bladder wall causes tumors to grow and the wall to thicken.
Thus for all non emergent exams a fasting period of 6 12 hours.